CBD is stealing the spotlight in the world of health foods and supplements. Underneath all the hype though, the reason CBD has stolen the show is due to how it works in the body; it strengthens the body’s endocannabinoid system.
Endocanna…….what? Yes its a tongue twister, but as you read on you’ll quickly realise how big of a deal the endcoannabinoid system is, and why everyone’s going gaga for CBD.
For simplicity, lets just call the endocannabinoid system the ECS from now on, ok?
What on Earth is the ECS?
The ECS is one of the least understood, but perhaps the most important systems in our bodies. It wasn’t even discovered until 1988, and were still trying to figure out the small print of what it does.
What we do know however, is that the main purpose of the ECS is to maintain balance (homeostasis) in the body. Homeostasis is the process by which the bodies internal environment is kept in consistent equilibrium, despite constant changes in the world outside.
Think of body temperature – when we go outside and its cold, our bodies need to respond and adjust accordingly. Core body temperature must be held in a sweet spot despite it getting colder outside. That’s the ECS at work.
The ECS functions in much the same way a thermostat would, turning biological activity up or down to meet the demands in response to the external environment.
Another example would be running. When you start running, the ECS ensures blood vessels dilate, breathing rate increases and core body temperature is maintained through sweating. This is all to maintain balance within, despite increased demands on the body.
This also applies for all sorts of other processes like metabolism, immune function, appetite, sleep and more. The ECS does it all; its the master regulator of all bodily processes. Its like the conductor of an orchestra – it makes sure all the bodily systems are playing in harmony.
Without the ECS co-ordinating all of our biology, all the bodily systems would be playing out of tune, and the beautiful harmony which keeps us fit and healthy would be lost.
To put it in practical terms, the ECS maintains our metabolism to prevent us from getting fat and diabetic, it controls our sleep so we can regenerate and repair, it co-ordinates our immune systems so we can fight infections. That’s just the start of it……
How Does The ECS Work?
Well, it all starts with Cannabis Sativa, which is home to hundreds of special molecules called cannabinoids. Oddly enough, these cannabinoids also occur naturally within every single one of us. The only difference is that they are produced within us (or endogenously), hence the name endocannabinoid.
The ECS is made up of two main parts:
- Endocannabinoids: messengers that communicate far and wide throughout the body – keys
- Cannabinoid receptors: receivers which translate messages into actions – locks
Together, these two parts make up a communication network that stretches across the whole body, and controls almost all of the bodies functions.
In order to deliver a message, endocannabinoids bind with receptors in much the same way a key fits into a lock.
So endocannabinoids act like keys and receptors act like locks.
Receptors are found on the surface of cells far and wide. When unlocked, a receptor passes on the message to its cell, which tells it to either wake the heck up, or chillllll out.
This basically means that the ECS can turn biological activity up or down across the whole body, in a similar way that a thermostat controls the heat in your whole house.
Two big responsibilities the ECS has is controlling our nervous and immune systems. The ECS controls the activity of neurotransmitters in the nervous system, like dopamine, serotonin, GABA and acetylcholine. These all influence the way we think, feel and act.
- Dopamine = pleasure and reward
- Serotonin = happiness and safety
- GABA = relaxation and rest
- Acetylcholine = memory and cognition
The ECS also influences how immune cells communicate, and ultimately the levels of inflammation in the body. Inflammation is a big player in human health and disease, so the ECS has an important role to play here.
Cannabinoid Receptors
There are two main cannabinoid receptors:
- Cannabinoid Receptor 1 (CB1)
- Cannabinoid receptor 2 (CB2)
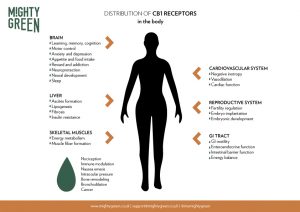
CB1 is found mostly in the brain and nervous system, but also in the:
- Liver
- Fat tissue
- Pancreas
- Muscle
- Gastrointestinal system
- Lungs
- Reproductive organs
CB2 is mainly found on cells of the immune system, but also in:
- The central and peripheral nervous system
- Bone making/degrading cells
- Skin nerves
- Skin cells
- Liver
- Pancreas
Cannabinoid receptors are like locks which are found on the outside of cells. These locks specifically recognise endocannabinoids, which are their respective keys. When unlocked, biological activity changes in a cell, which corresponds to changes in:
- Appetite
- Sleep
- Mood & Emotion
- Memory
- Cognition
- Energy metabolism
- Thermoregulation
- Digestion
- PH Balance
- Blood Pressure
- Pleasure & Reward
- Pain
- Reproduction
- Inflammation
- Immune function
The ECS in Health and Disease
Everyone has a different ECS activity based on their genetics, how they live their lives and their environments. Sadly our ECS can fall out of balance, which means our bodily systems also struggle to keep us healthy.
There are several things which can upset the way the ECS works. Modern life – one thats especially far removed from how we as humans used to live, can be stressful for the ECS. This makes it hard for the ECS to keep us healthy.
These include:
- Stress
- Sleep deprivation
- Poor diet
- Sedentary lifestyle
- Infection
In certain cases, peoples ECS can become dysregulated due to how their genetics, lifestyle and environment are interacting. The ECS can become both over and under active, which upsets the balance of homeostasis in different ways.
That basically means the conductor isn’t keeping the instruments (bodily systems) in harmony, they’re playing out of tune. Not gooooood.
An under active ECS, or clinical endocannabinoid deficiency (CECD) may play a role in mood disorders, IBS and migraines (Russo, 2016). On the flipside, an overactive ECS may play a role in arthritis, obesity and problems with blood sugar.
Researchers are still trying to figure out whether the ECS is dysreguated as a result of disease, or if it is promoting disease. We just don’t know yet.
The emergence of medical conditions often requires more than just one bodily system to become imbalanced. Take IBS for example; as well as digestive issues there are often problems with sleep, mood and fatigue. That means the immune, digestive, nervous and and hormone systems may not be working properly.
It makes sense to hypothesise then, that if all these systems are imbalanced at once, that may have something to do with the ECS, since it’s the master regulator of bodily systems.
The ECS, CBD and Cannabinoids
Cannabinoids from plants are so scarily similar to endocannabinoids, they’re basically siblings. They are keys that fit the same locks, and can perform some of the roles that endocannabinoids can in the body; ensuring balance across the bodily systems.
This may have something to do with the tidal wave of interest in plant cannabinoids such as CBD. People are using it for all sorts of ailments, from pain to anxiety.
CBD actually prevents the breakdown of one of our endocannabinoids, known as Anandamide. This means there’s more Anandamide available for our cells to soak up. More anandamide provides mood boosting, anti-inflammatory and pain relieving effects.
CBD can also block cannabinoid receptors CB1 and CB2, which alters how messages are received by endocannabinoids.
So, CBD can both turn up and turn down the ECS, based on each individuals need to turn their ECS up or down.
It might be that cannabinoids like CBD could help support the function of an ECS that is struggling to maintain homeostasis in certain medical conditions.
It makes sense if you look at what roles the ECS has, and the fact that cannabinoids push many of the same buttons that endocannabinoids do.
References
Russo, E. B. (2016) ‘Clinical Endocannabinoid Deficiency Reconsidered: Current Research Supports the Theory in Migraine, Fibromyalgia, Irritable Bowel, and Other Treatment-Resistant Syndromes’, Cannabis and Cannabinoid Research, 1(1), pp. 154–165. doi: 10.1089/can.2016.0009.

